Leveraging both commercially available conventional LNP delivery systems and proprietary platforms (including novel LNPs and ligand-mediated systems), ENO Bio has developed corresponding liquid formulation technologies for each. By incorporating a post-mixing encapsulation process, the company enables high-quality production of co-encapsulated liquid formulations for multiple mRNA sequences, as well as mRNA/sgRNA or mRNA/siRNA mixtures. This capability meets essential development and clinical trial needs for mRNA products targeting seasonal or emerging disease prevention and personalized therapies.
Addressing the inherent thermal instability of mRNA liquid formulations, ENO Bio has pioneered a global breakthrough with its mRNA lyophilization technology. This innovation significantly enhances the thermal stability of various LNP- and non-LNP-delivered mRNA formulations. The technology has been successfully applied to the high-quality production of co-encapsulated lyophilized products, including those with multiple mRNA sequences or mRNA/sgRNA/siRNA mixtures. This advancement better supports clients in developing and commercializing mRNA products suited for broader, more universal application scenarios.

The poor stability of mRNA liquid formulations presents a major challenge in mRNA drug development, significantly limiting the distribution and quality standards of mRNA products. For instance, Moderna's mRNA-1345 vaccine requires storage at -20°C, with mRNA integrity declining to 50% after 18 months. Similarly, Pfizer's BNT162b2 vaccine must be stored between -80°C and -60°C and remains stable at room temperature for only 2 hours after thawing. These stringent storage conditions and limited stability restrict the clinical accessibility of mRNA-based medicines.
The inherent instability arises from multiple factors: mRNA contains numerous sites susceptible to hydrolysis and enzymatic degradation, leading to poor natural stability in aqueous solutions. LNPs, as electrically neutral nanoparticles, are prone to rupture and fusion during transportation. Furthermore, lipids within LNPs—particularly ionizable lipids—are often designed with degradable structures to enhance in vivo metabolism and reduce toxicity, but this inherent lipid instability further compromises the overall stability of the mRNA drug.
To address these challenges, several strategies can be employed. AI algorithms can optimize mRNA sequences to select thermodynamically more stable variants. LNP formulations can be improved by incorporating a certain proportion of PEG lipids to enhance physical stability. Additionally, adding suitable cryoprotectants and buffer salts can slow the oxidation and hydrolysis of mRNA and lipids. While these optimizations provide some improvement in formulation stability, they remain insufficient for scenarios requiring higher stability standards.
To further overcome the stability challenges of mRNA formulations, ENO Bio has developed an advanced mRNA lyophilization technology. This process preserves the structural integrity of the sample through freeze-drying while gently removing free water and oxygen to prevent lipid oxidation and hydrolysis. By solidifying the formulation, it also reduces nanoparticle thermal motion, thereby enhancing stability.
However, due to the complex composition of lipid nanoparticles and their sensitivity to freezing and drying conditions—particularly the stress induced by lyophilization, which can easily disrupt the structure of large nucleic acid molecules—conventional freeze-drying methods are unable to maintain the stability and bioactivity of mRNA-LNP formulations.
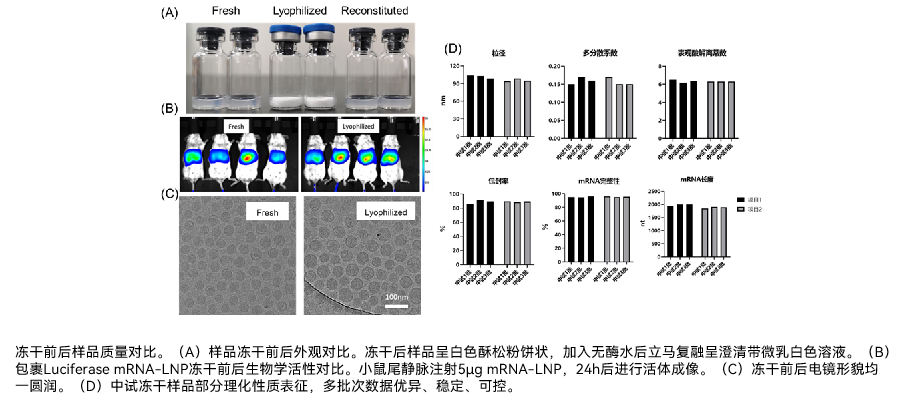
ENO Bio has addressed this challenge through Design of Experiments (DOE) methodology, systematically evaluating the effects of various cryoprotectants, their concentrations, and lyophilization cycles on the final product. Based on these studies, the company has established a robust mRNA-LNP and mRNA lyophilization platform. This platform has successfully produced lyophilized formulations using commercially available LNPs, proprietary LNP systems, and proprietary ligand-mediated mRNA delivery systems.
The resulting lyophilized formulations are characterized by excellent reconstitution properties, maintaining consistent physicochemical characteristics and biological activity before and after freeze-drying. Most significantly, they demonstrate substantially improved thermal stability, enabling storage and transportation under standard cold chain conditions (2-8°C) or even at room temperature. This breakthrough greatly enhances the accessibility and distribution potential of mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
This lyophilization process has already been implemented across several pipelines at ENO Bio and with collaboration partners, successfully supporting multiple clinical registration submissions and Phase I clinical trials or investigator-initiated trials (IIT). The technology's efficacy and safety have been extensively validated across different product candidates.