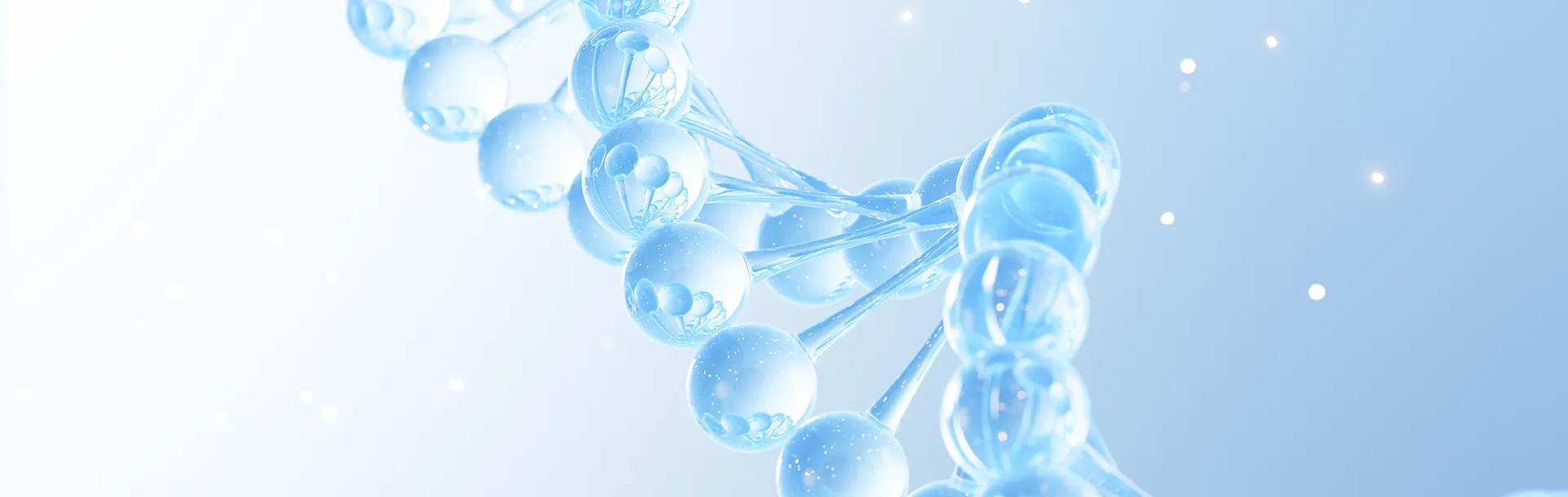

ENO Bio integrates AI technology into mRNA drug design by aligning with the technical characteristics of mRNA and evolving trends in pharmaceutical development. This approach encompasses the entire process, from target discovery and protein sequence design to mRNA sequence design. The company utilizes comprehensive, real-time validation data generated from high-throughput mRNA synthesis and design sequences, along with real-world data accumulated from numerous product development cases, to drive continuous iteration of its AI algorithms.
The AI and mRNA co-driven target discovery and drug design technology developed by ENO Bio not only assists clients in developing mRNA drugs against known protein targets—enabling highly efficient, druggability-oriented design of proteins and mRNA sequences while achieving intellectual property breakthroughs—but also facilitates pioneering target discovery and screening at the source, advancing the research and development of various innovative mRNA-based therapeutics.
Target Discovery and Protein Sequence Design
Target discovery and protein sequence design serve as the "core foundation and critical starting point" for mRNA drug development. The function of the protein encoded by the mRNA directly determines the therapeutic efficacy of an mRNA drug. This is particularly evident in complex diseases such as cancer—for instance, in the context of tumor neoantigens—where identifying the optimal target and designing a protein with high biological activity and favorable stability is a complex, time-consuming, and empirically driven process. Conventional methods often struggle to handle vast biological datasets and intricate protein folding mechanisms. In contrast, AI possesses the capability to efficiently analyze multi-dimensional biological data, accurately predict protein structures, and optimize sequences, thereby significantly reducing development risks, accelerating timelines, and facilitating the discovery of novel targets and the design of improved therapies.
When it comes to experimental validation and data feedback, traditional protein technology platforms are limited by challenges in protein expression and purification, resulting in nearly two-thirds of designed sequences being unobtainable. This limitation impedes comprehensive and effective validation. mRNA technology effectively overcomes this barrier by enabling the synthesis and testing of virtually any designed sequence, thereby providing complete, real-world data feedback and substantially enhancing the efficiency and probability of successful target discovery.
The AI tools developed by ENO Bio standardize functional modules—such as antigenic epitopes, enzymatic cleavage sites, signal peptides, and de-immunization design modules—enabling rapid adaptation to the diverse druggability optimization requirements of different targets and disease contexts. This approach effectively balances the clinical safety and industrialization needs of protein-based therapeutics, facilitating the efficient translation of drug candidates from research to application.
Locally deployed protein structure and sequence databases including UniRef90, MGnify, and PDB
provides structure- and sequence-based search and alignment services
phylogenetic tree construction services


Long-Acting Protein Design
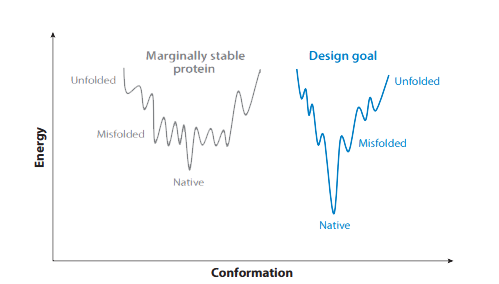
Our AI-driven design algorithm optimizes protein folding free energy, enabling proteins to spontaneously fold more readily into their functional native state. This enhancement significantly improves protein stability and facilitates the development of long-acting therapeutic candidates.
Protein Humanization Design
By integrating evolutionary homology analysis with AI-based design tools, we enhance the sequence similarity of proteins to human counterparts, thereby reducing potential immune responses to protein therapeutics in humans.
The mRNA sequence itself plays a critical role in the overall druggability of a therapeutic agent. A well-designed mRNA sequence ensures efficient translation initiation, optimal stability, and controllable immunogenicity—factors that directly influence protein yield, expression duration, and treatment safety. However, mRNA sequence optimization is a complex task due to intricate interactions involving codon preference, secondary structure, and the interplay between the coding sequence (CDS) and untranslated regions (UTRs). Unoptimized sequences may result in low protein expression, rapid degradation, or unintended immune activation, thereby compromising therapeutic efficacy. Artificial intelligence offers an effective solution to this multi-faceted challenge by enabling precise, multi-objective optimization of mRNA sequences to maximize therapeutic effect and enhance druggability.
ENO Bio's proprietary AI-driven sequence optimization algorithm, RheDesign, focuses on multi-dimensional optimization and functional refinement of the CDS. It simultaneously balances translation efficiency, protein folding capability, and immune compatibility through dynamic codon usage modeling, secondary structure avoidance and remodeling, and function-oriented modular design. In practice, RheDesign has significantly increased the expression levels of target proteins (e.g., EGFP), demonstrating superior translation efficiency and stability compared to commercially available tools. This technology effectively addresses common challenges in mRNA drug development, such as low translation efficiency and protein misfolding, providing robust support for the creation of highly expressive and potent mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
Building on its core CDS optimization capabilities, RheDesign further incorporates UTR co-design, effectively overcoming issues associated with traditional independent CDS-UTR design—such as translational instability and poor tissue specificity—thereby significantly enhancing mRNA expression levels and functional consistency. As illustrated in the accompanying figure, for the expression of a specific cytokine, mRNA sequences designed using RheDesign achieved more than a 3-fold increase in protein expression compared to conventional methods. This approach is particularly suitable for mRNA vaccines and therapeutics requiring precise temporal expression control and targeted delivery, demonstrating strong clinical translation potential and industrial advantages.