The design and production of transcription templates form the foundation of mRNA drug manufacturing. While the coding sequence (CDS) directly determines the structure of the expressed protein, regulatory elements such as untranslated regions (UTRs) and the Poly(A) tail significantly influence mRNA translation efficiency and stability. Consequently, the strategic design and selection of UTR and Poly(A) sequences are critical factors in transcription template design.
ENO Bio possesses mature capabilities in transcription template design and production, as well as expertise in designing and screening regulatory elements like UTRs and Poly(A) tails. This enables the flexible application of various conventional elements and manufacturing techniques to design and produce high-quality transcription templates tailored to client requirements.

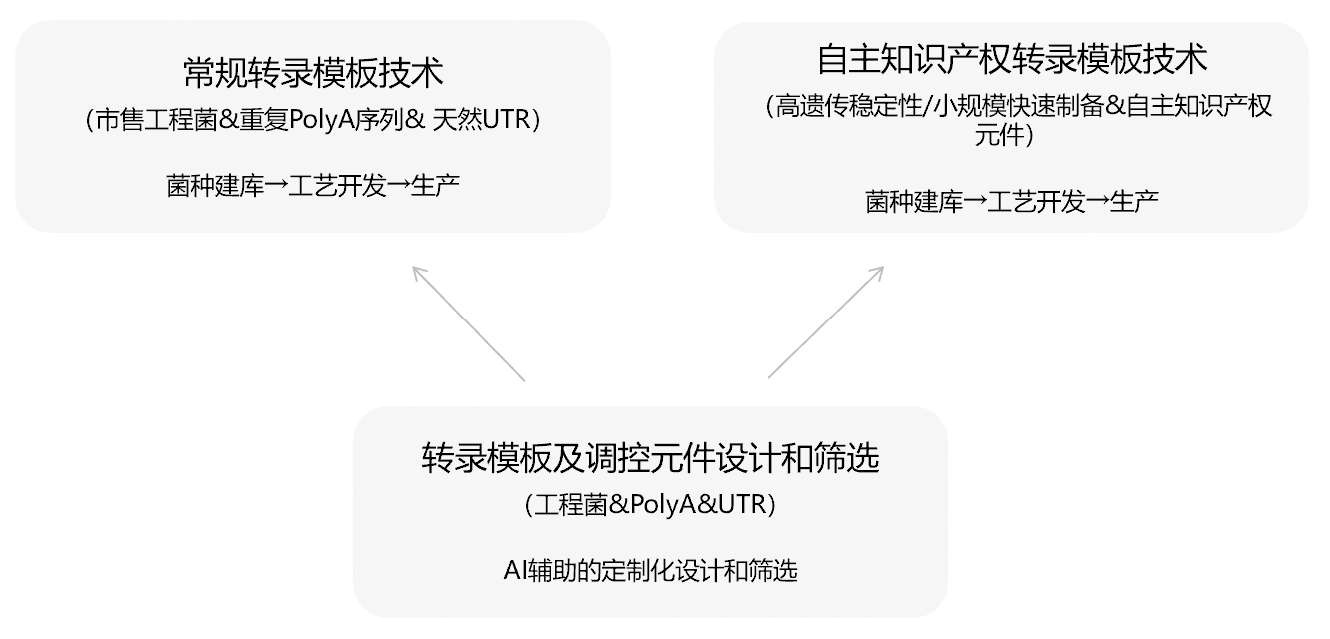

ENO Bio's proprietary technology for high genetic stability in plasmid templates has been successfully implemented in numerous mRNA product development programs. These include mRNA vaccines for herpes zoster, bivalent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), tuberculosis, personalized cancer, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma, as well as an mRNA therapeutic for osteoarthritis. This technology addresses the critical client needs for robust intellectual property and superior plasmid genetic stability, and has contributed to these candidates successfully obtaining clinical trial approvals.
ENO Bio leverages AI models to functionally annotate vast libraries of both natural and rationally designed UTR sequences. This enables the rapid, systematic characterization of UTR properties and quantifies their impact on key parameters such as mRNA half-life, translation efficiency, and immunoevasion capacity. By constructing multi-dimensional performance profiles, ENO Bio can effectively guide the selection and design of UTRs for specific applications.
Building on this foundation, the company has established a core capability for AI-driven screening of natural UTRs to meet fundamental mRNA drug development needs. This capability has been extended to include AI-powered custom UTR sequence design and the creation of a proprietary UTR library, addressing the need for advanced druggability optimization and UTR sequence intellectual property breakthroughs for a wider range of client mRNA therapeutics.
ENO Bio's proprietary UTR library encompasses a diverse range of tissue and cell types, offering broad applicability and the potential for tissue or cell specificity. It demonstrates excellent development and application capabilities, including:
